Sintered Felt
HOME / SCREEN MESH MATERIALS / Sintered Felt
Sintered Felts | Metal & Stainless Steel Sintered Fiber Felt Manufacturer
Sintered felts represent a sophisticated class of porous metal media, formed by layering and bonding fine metal fibers (or foaming metal substrates) via high-temperature sintering. This manufacturing approach yields a three-dimensional, interconnected pore network with high porosity, excellent permeability, uniform pore size distribution and outstanding mechanical integrity. Resources show that porosity can reach up to ~85% in many systems.
Such materials deliver a unique combination of filtration depth (capturing particles inside the material bulk), mechanical robustness, thermal and chemical resistance, and the ability to be cleaned and reused. They are increasingly preferred over conventional woven wire mesh or polymeric media in demanding industrial applications.

Why Sintered Felts Matter – Key Benefits & Innovations
1. Exceptional Porosity & Low Pressure Drop
Thanks to the sintered fiber network structure, these felts offer extremely high porosity (often 60–85% or more) and excellent through-flow characteristics. For example, one data set shows 85% porosity with the potential for 20× higher flow compared to traditional media.
This means for the same face area you can achieve higher throughput or lower pressure drop — a win in energy-sensitive or high-flow systems.
2. Uniform & Stable Pore Structure – Depth Filtration Capability
Unlike plain woven meshes which provide surface filtration, sintered felt offers depth filtration, meaning contaminants are trapped within the volume of the material, not just on the surface.
In-depth capture means less frequent replacement or cleaning downtime.
3. High Mechanical Strength & Thermal / Chemical Robustness
The sintered bond of metal fibers ensures high strength (in some cases up to tens of MPa breaking strength) and good performance under thermal shock and mechanical stress.
Many variants survive elevated temperatures (for example, standard stainless felt up to ~600 °C, FeCrAl up to ~1000 °C) and aggressive chemical environments.
This makes them ideal for high-temperature filtration, hot gas or liquid streams, and corrosive process environments.
4. Cleanability & Reusability
Because of their open-cell and robust structure, sintered felts can often be cleaned (via back-flush, back-pulse, ultrasonic cleaning, chemical cleaning) and re-used, significantly reducing lifecycle cost and waste.
This is especially valuable in continuous process systems, where downtime is costly.
5. Tailor-Made Layering & Composite Designs
Innovations now allow multi-layer or graded structures (different pore sizes stacked) and composite designs (e.g., fiber felt sintered onto woven mesh or foam core) to optimise for gradient filtration, high dirt holding capacity, and durability.
Core Applications – Where Sintered Felts Excel
Because of their versatility, the sintered felts category spans many industrial domains:
- Polymer & plastic melt filtration, resin purification
- Petrochemical, chemical process streams (liquid & gas) including high-temperature / high-corrosion environments
- Hydraulic and lubrication oil filtration in heavy-machinery or aerospace systems
- Hot gas filtration, dust collection in power generation or heavy industries
- Gas diffusion layers (GDL) for hydrogen & fuel-cell systems, catalyst support media
- Marine, offshore, and seawater filtration (especially titanium variants)
- Battery, electrochemical or energy-storage systems (foam/nickel media)
- Exhaust systems, heat-transfer components, acoustic or vibration damping in aeronautics
These diverse applications reflect the broad potential for sintered felts — their capability to combine filtration, flow management, structural support and thermal/chemical resistance in one material package.
Materials & Product Scope
Sintered felt is manufactured from fine metal fibers such as stainless steel, FeCrAl, titanium, nickel, and other alloys. These micro-diameter fibers are evenly distributed through a controlled non-woven laying process, laminated in multiple layers, and then sintered at high temperature to form a strong porous structure.
Based on the base material used, sintered felt is typically classified into stainless steel sintered felt, titanium sintered felt, nickel sintered felt, and other specialized metal types.
Stainless Steel Sintered Fiber Felt
Built from 304/316L stainless steel fibers; excellent corrosion resistance, great for chemical, food, pharmaceutical, hydraulic markets.

Sintered Nickel Fiber Felt
Pure nickel fiber construction for higher temperature and more aggressive chemistries (acid/alkali, hydrogen systems).

Sintered Titanium Fiber Felt
Titanium fiber felt offers ultra-lightweight, high corrosion resistance (e.g., seawater, marine, biocompatible), useful in niche sectors.
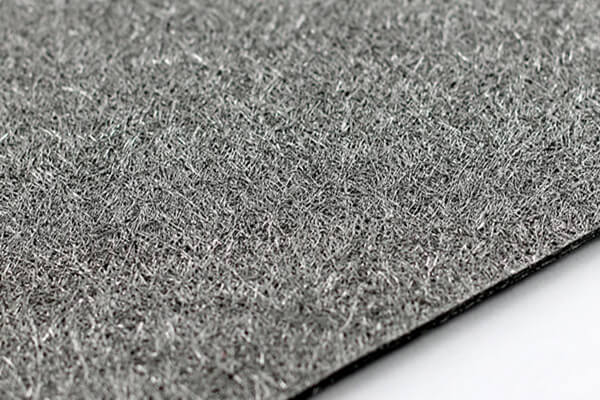

Sintered FeCrAl Fiber Felt
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum alloy fiber felt optimized for high-temperature (> 1000 °C) and electrically conductive applications (heating elements, exhaust purification).
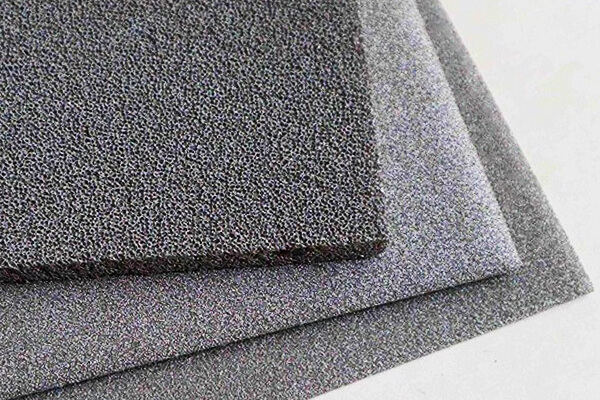

Nickel Foam
A 3D open-cell nickel foam rather than fiber felt; serves as high-conductivity, high-porosity support media in batteries, fuel-cells, catalytic carriers and advanced filtration.
