Knitted Mesh Mist Eliminators | Demister Pads
HOME / MESH FILTER ELEMENTS / Knitted Mesh Filters and Components / Knitted Wire Mist Eliminator
Knitted Mesh Mist Eliminator | Knitted Mesh Wire Mesh Demister Pads
A Knitted Wire Mesh Mist Eliminator (also known as a demister pad) is a highly efficient mechanical separation device designed to remove entrained liquid droplets and aerosols from gas or vapor streams. Its widespread adoption across industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, petrochemical refining, and power generation is driven by its exceptional performance in protecting downstream equipment, improving process efficiency, recovering valuable products, and ensuring compliance with environmental emissions standards.
Our industry-proven mist eliminators are engineered for superior performance, consistently demonstrating the capability to effectively capture and remove micron-sized mist, with high removal efficiency for droplets as fine as 2 microns in many applications. This high degree of separation is achieved while maintaining an exceptionally low pressure drop, typically less than 2.5 mbar for standard pads, ensuring energy-efficient operation and minimizing the load on associated systems.
Structure of Knitted Mesh Mist Eliminators
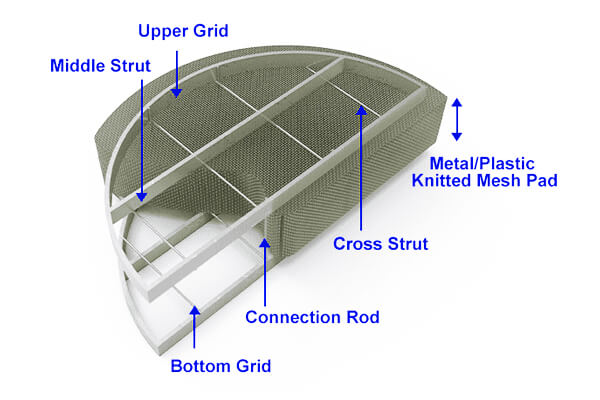
The Knitted Wire Mesh Mist Eliminator is a fully assembled, engineered module designed for robust and reliable performance. Its structure is not merely the mesh pad itself, but a complete mechanical assembly that ensures proper installation, structural integrity under operational loads, and optimal gas-liquid flow dynamics. The standard assembly typically consists of the following key components:
1. Metal/Plastic Knitted Mesh Pad
This is the functional core of the assembly. It is a three-dimensional, highly porous structure fabricated by interlooping fine metal or plastic wires into a resilient pad. This unique knitting method creates a vast surface area within a high void volume (typically >97%), providing the tortuous path necessary for droplet impaction and coalescence. The material (e.g., SS316, PP, PTFE) is selected for chemical compatibility with the process stream.
2. Support Grids (Upper Grid & Bottom Grid)
These are sturdy, perforated or bar-type grids that sandwich the mesh pad.
The Bottom Grid acts as the primary load-bearing platform, installed on permanent supports within the vessel. It holds the full weight of the mesh pad and any accumulated liquid.
The Upper Grid is placed on top of the mesh pad, serving to contain and stabilize the pad, preventing movement or fluffing under high gas velocity. Both grids are designed with maximum open area to minimize initial pressure drop.
3. Internal Reinforcement (Middle Strut & Cross Struts)
To prevent buckling or deformation of the mesh pad—especially in large-diameter vessels or under significant differential pressure—internal reinforcement is integrated.
Middle Struts and Cross Struts are strategically positioned within the pad thickness or between support grids. They provide critical internal bracing, maintaining uniform pad density and preventing channeling of the gas stream, which would compromise separation efficiency.
4. Assembly Hardware (Connection Rods)
All components are securely fastened into a single, manageable unit using Connection Rods (tie rods). These rods vertically connect the upper grid, internal struts, and bottom grid, compressing the mesh pad to a specified thickness and ensuring the entire assembly behaves as one rigid structure during handling and installation. This allows the complete demister module to be easily installed or removed through vessel manways.
Working Principle of Knitted Mesh Mist Eliminators
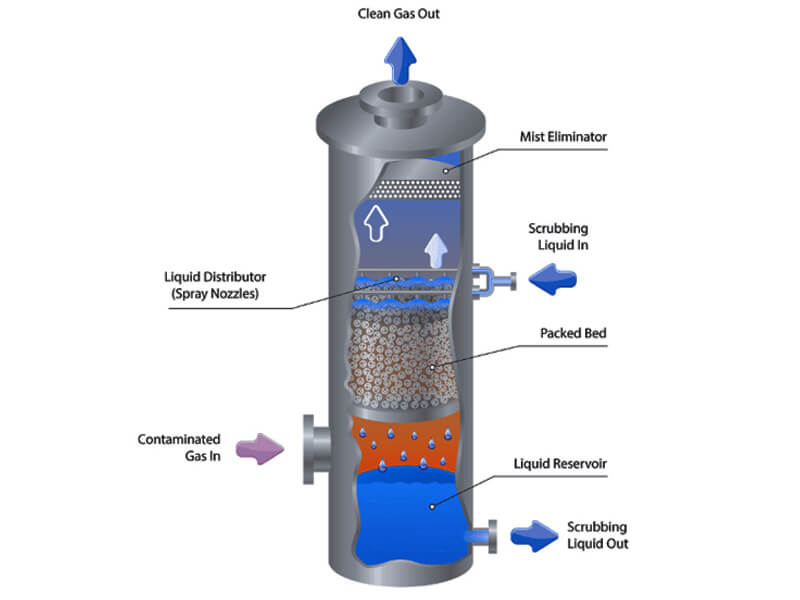
When a vapor stream carrying entrained liquid droplets passes through the layered mesh structure of a knitted wire mist eliminator, a selective separation process occurs. Due to their significantly higher inertia compared to the vapor molecules, the liquid droplets cannot follow the gas streamlines around the wire filaments. Instead, they impact and adhere to the extensive wire surface area. These captured droplets coalesce upon contact, merging into progressively larger masses. Once the combined droplets reach a sufficient size, gravitational force overcomes the vapor drag and surface adhesion, causing them to drain from the mesh. The vapor continues through the pad with minimal obstruction, resulting in a purified overhead stream that is effectively free of liquid carryover.
Materials Available of Knitted Mesh Mist Eliminators
Material selection is dictated by corrosion resistance, temperature, and process fluid compatibility.
Metallic: Stainless steels (304, 316, 316L) are most common. Special alloys like Monel, Inconel, Hastelloy, and Titanium are used for chlorides, high temperatures, or severe corrosion.
Non-Metallic/Polymers: Polypropylene (PP), Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and Polyvinylchloride (PVC) are used for highly corrosive chemical services (e.g., chlor-alkali, strong acids) where metals are unsuitable.
Advantages of Knitted Mesh Mist Eliminators
Knitted wire mesh mist eliminators deliver superior performance through an optimal balance of efficiency and practicality, offering distinct benefits for industrial separation processes.
High Efficiency & Coalescence: Achieves removal rates exceeding 99% for droplets as fine as 3-5 µm by merging them into larger drops for easy drainage.
Low Pressure Drop: Its high void volume (>97%) ensures minimal flow resistance, typically under 25 mmWG, reducing energy costs.
High Capacity & Reliability: Handles high gas velocities and variable loads with robust, corrosion-resistant construction for long service life.
Easy Maintenance: Pads are cleanable in-place or removable, minimizing downtime and operational disruption.
Design Flexibility: Fully customizable in shape, size, material (metals/polymers), and density to fit specific vessel and process needs.
Cost-Effective: Provides high performance at a competitive lifecycle cost due to low initial investment, energy use, and maintenance.
Specification of Knitted Mesh Mist Eliminators
1. Mesh Style & Performance Classification
This table categorizes the mist eliminators by their internal mesh structure, density, and intended application.
| Mesh Type | Application Profile | Wire Diameter | Bulk Density | Void Fraction | Surface Area | Separation Efficiency |
| Standard Duty | General Purpose (Distillation, Knockout Drums) | 0.25 – 0.28 mm | 144 kg/m ³ | ~ 98.0% | ~ 280 m²/m³ | 99.9% @ ≥ 5–10 µm |
| High Efficiency | Fine Mist Removal (Absorption, Acid Plants) | 0.10 – 0.15 mm | 192 – 240 kg/m ³ | ~ 97.5% | 400 – 500 m²/m³ | 99.9% @ ≥ 3 µm |
| High Capacity | Fouling Service / Viscous Liquids / High Velocity | 0.28 – 0.35 mm | 80 – 112 kg/m ³ | > 99.0% | 150 – 200 m²/m³ | 99.9% @ ≥ 10 µm (Resists plugging) |
| Co-Knit (Dual) | Ultra-Fine Mist / Fog (Bonded with Fiber) | Metal + Fiber Yarn | 350 – 600 kg/m ³ | Low | Very High | 99.9% @ ≥ 1 µm |
2. Physical & Dimensional Specifications
This table defines the structural manufacturing standards, tolerances, and grid details.
| Feature | Specification Details |
| Pad Thickness | Standard: 100 mm (4″) or 150 mm (6″) <br> Custom: 25 mm to 300 mm available upon request. |
| Pad Configuration | One-Piece: For Vessel ID < 600 mm <br> Segmented: For Vessel ID > 600 mm (Sections sized for 18″/24″ manways). |
| Shape Options | Circular, Rectangular, Annular (Donut), Kidney-shape, Custom geometric. |
| Construction Method | Layered and crimped wire mesh; layers usually cross-stacked at 90° or 45°. |
| Dimensional Tolerance | Thickness: ± 3 mm <br> Diameter: +3 mm to +25 mm (Oversized for compression fit). |
| Grid (Support) Type | Top and Bottom Open Grids (welded to mesh or captured). |
| Grid Materials | Typically matches the mesh alloy (e.g., 316L Mesh utilizes 316L Grids). |
| Grid Dimensions | Flat Bar: 25 mm x 3 mm (standard) <br> Round Rod: 6 mm diameter <br> Open Area: > 90% to minimize flow restriction. |
3. Material Selection Guide
A quick reference for selecting materials based on operating conditions.
| Material Category | Common Grades | Typical Operating Limits |
| Stainless Steel | 304, 304L, 316, 316L, 321, 410S | Up to 400°C – General Chemical / Water / Oil |
| Nickel Alloys | Monel 400, Inconel 600/625, Hastelloy C276 | High Temp & Severe Corrosion (Acids, Chlorides) |
| Reactive Metals | Titanium Gr. 2 | Extreme Seawater / Oxidizing Acid Resistance |
| Synthetics (Plastics) | PP (Polypropylene) | Max 80°C – Low cost, good chemical resistance |
| Fluoropolymers | PTFE, PVDF, ETFE | Max 200°C+ – Ultra-high chemical inertness |
4. Operational Design Parameters
Key engineering data for process calculation.
| Parameter | Standard Value / Range |
| Design Pressure Drop | Typically < 250 Pa (25 mm WC) in clean conditions. |
| Max Rec. Pressure Drop | 500 Pa (50 mm WC) – Cleaning/Maintenance recommended. |
| Operating Velocity (K-Value) | Standard Stainless Mesh: 0.107 m/s (0.35 ft/s). |
| Turndown Ratio | Typically efficient down to 30% of design flow. |
Applications of Knitted Mesh Mist Eliminators
1. Oil & Gas Industry
In upstream extraction, midstream transport, and downstream refining, mist eliminators are standard equipment.
- Three-Phase Separators: Installed in the gas outlet of oil/gas/water separators to prevent crude oil carryover into the gas line.
- Knockout Drums (K.O. Drums): Used to remove bulk liquids from gas streams during process upsets or normal operation.
- Compressor Suction Drums: Critical for removing liquid droplets before gas enters a compressor. Liquid ingestion can cause catastrophic blade failure or cylinder damage.
- Glycol Dehydration Towers: Placed at the top of the contactor tower to prevent the loss of expensive glycol (used to dry natural gas) into the pipeline.
- Amine Sweetening Plants: Located in the absorber and regenerator columns to minimize amine solvent losses (chemical carryover).
2. Petroleum Refining
Refineries rely on mist eliminators to maintain efficiency and safety in fractionation processes.
- Vacuum Distillation Towers: Installed to remove heavy hydrocarbon droplets and metals (like asphalt or coke fines) from the gas oil. This prevents contamination of the catalyst in downstream Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) units.
- Fractionating Columns: Used at the top of the column to prevent product loss and ensure the distilled vapor meets purity specifications.
- Lube Oil Refineries: Used in solvent extraction towers to separate solvents from the oil.
3. Chemical & Petrochemical Processing
- Evaporators: Installed to prevent the carryover of dissolved solids or boiling liquid into the condensate or vapor line, ensuring the purity of the distilled water or solvent.
- Absorption Columns: Used to prevent the scrubbing liquid (absorbent) from escaping with the treated gas.
- Steam Drums: Essential in boilers to separate water droplets from steam. Dry steam is required to prevent erosion of turbine blades and superheater tubes.
4. Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) & Power Generation
- FGD Scrubbers: In coal-fired power plants, limestone slurry is sprayed to remove sulfur dioxide. Mist eliminators (often dual-layer or chevron/mesh combinations) remove the slurry mist to prevent downstream corrosion, duct scaling, and “stack rain.”
- Geothermal Power Plants: Steam separators use mesh pads to remove brine and rock particles from steam before it enters the turbine.
5. Desalination Plants
- Multi-Stage Flash (MSF) Evaporators: Mist eliminators are critical here. They separate brine droplets from the water vapor. If brine carries over, the salinity of the produced fresh water increases, failing quality standards.
6. Sulfuric Acid Production
- Drying Towers: Mesh pads (often co-knit with Teflon/PTFE or glass fiber) prevent sulfuric acid mist from entering the blower and heat exchangers.
- Absorption Towers: Used to capture acid mist formed during the absorption of SO₃, protecting the environment and recovering acid.
7. General Environmental & Industrial Applications
- Air Scrubbers: Used in various manufacturing plants (plating, chemical etching) to neutralize acidic or alkaline exhaust fumes. The mist eliminator ensures the neutralizing liquid remains in the scrubber.
- Compressed Air Systems: Used in after-coolers to remove condensed water and oil from compressed air lines.
- Nitric Acid & Fertilizer Plants: Used to recover platinum catalyst dust and prevent acid mist emissions.
Request A Quote
* indicates required fields
